Maintenance covers all measures to maintain the equipment in good operating condition to preserve the serviceability of the equipment.
- The process of keeping something in good condition.
Types of Maintenance
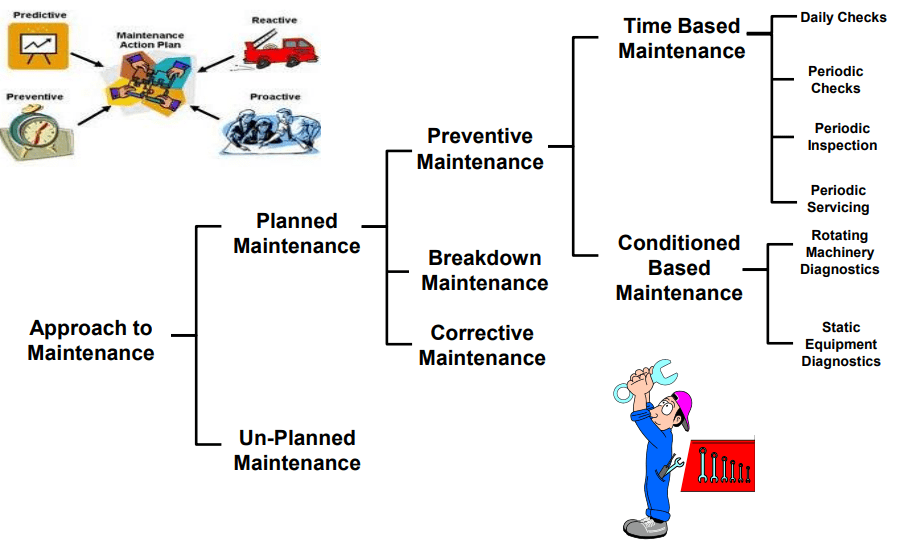
Objectives of Maintenance
Productivity Improvement through maximum availability at optimum cost
- Reduce idle hours due to component malfunctioning
- Maximize operational efficiency
- Ensure safety during the operation
- Prevent breakdown during operation
- Elimination of future defects
- Forestall rapid wear of components
- Enhance performance level
Why Maintenance?
- To enhance the Life Cycle of Equipment
- To Maximize the equipment
Effectiveness by eliminating 7 Big Losses;
1-Breakdowns due to equipment failure
2-Set up and unnecessary adjustments
3-Idling and Minor Stops
4-Running at Reduced Speed
5-Start-up Losses
6- Loss on Account of Tool Change
7- Rework and Scrap
- To control the Quality Problems
- To Minimize or the Eliminate the Waste
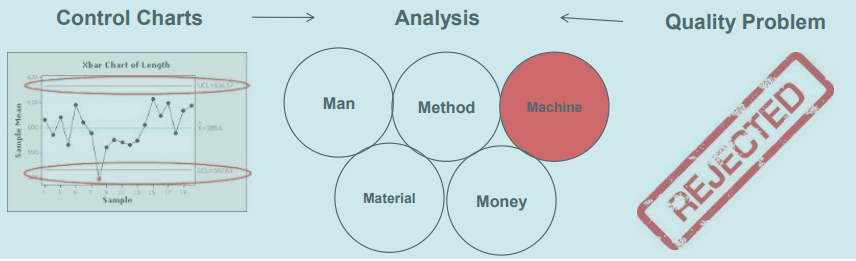
What is Waste?
Resources Consumption for any goal/purpose/objective other than the creation/addition of value for the end customer.
Type of Wastes
Muda, Mura, Muri
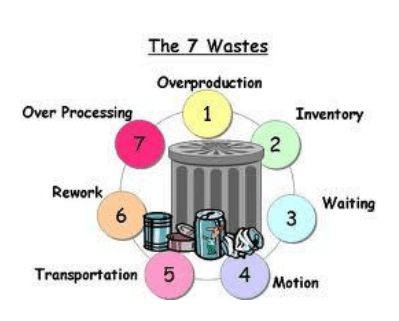
In the context of lean thought, there are seven main types of waste, which are often called the “7 Wastes”:
- Overproduction- Avoid overproduction by balancing supply to demand
- Unnecessary Inventory – Avoid Wastages of Space and Effort
- Unnecessary Delay – Avoid Wastages Delay caused by unsynchronized activities
- Unnecessary Motion – Avoid Wastages being caused by unnecessary movements or unergonomic process designs
- Transportation – Avoid Wastages being caused by unnecessary Material movements
- Unnecessary Rework/Defects – Avoid wastages of value-added time
- Over-Processing – Avoid waste of unnecessary processes
How to Control Wastes?
By Implementation of;
- Work Study & Method Engineering
- Motion Study
- Time Study
- Supply Chain Management
- Supplier Quality Assurance etc
- Inventory Control
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) – Equipment Effectiveness
- Total Quality Management (TQM) – Continuously Improving the Quality
- Ergonomics– Study of Human Factor
- Operations Research– Optimization of Process-Optimal Solution of Complex Decisions
- 5S – seiri, seiton, seiso, seiketsu, and shitsuke



