Basically, there are two types of maintenance in manufacturing
- Planned Maintenance
- Un-Planned Maintenance
Planned and unplanned maintenance are two approaches that play an important role in managing, machinery services and equipment in manufacturing. The maintenance strategies, processes, and objectives influence the manufacturing operations of an industry.
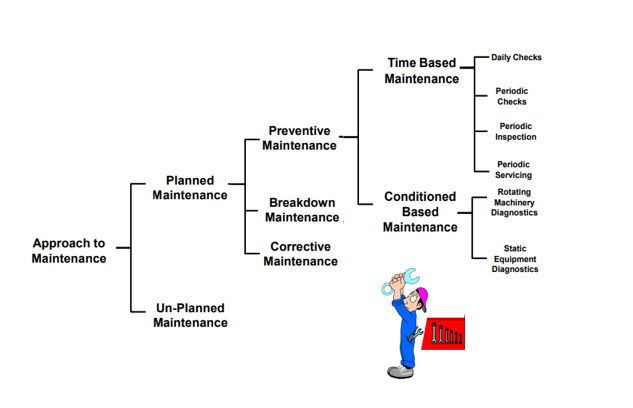
Preventive Maintenance
Time-based maintenance refers to a maintenance strategy that involves conducting maintenance activities at predetermined intervals, regardless of the equipment’s condition. This approach is commonly used in many industries for safety reasons
The fixed periods for TBM activities can be categorized into daily, weekly, monthly, yearly, or any other specified timeframe. The activities of TBM may include daily checks, periodic checks, periodic inspections, and periodic servicing.
Condition-based maintenance (CBM) is a maintenance strategy that involves monitoring the condition of an asset or system in order to determine the optimal time for maintenance activities. This approach
Online Basis: This study is conducted using data collected through online sources and platforms. Based on Various Measurement Data and Its Analysis: The findings of this study are derived from the analysis of diverse measurement data collected from many sources.
The level of deterioration and so forth.
Predictive maintenance refers to a proactive approach in the field of maintenance management, where advanced techniques and technologies are employed to predict and prevent
Rotating machinery diagnostics and static equipment are two areas of study within the field of industrial engineering. Diagnostics involve the utilization of recorded data on the amount of wear or degradation in order to make predictions.
Vibration analyzers and ultrasonic meters are two types of instruments often used in many industries for diagnostic and measurement purposes.
The dataset provided pertains to the operational time of a statistical service.
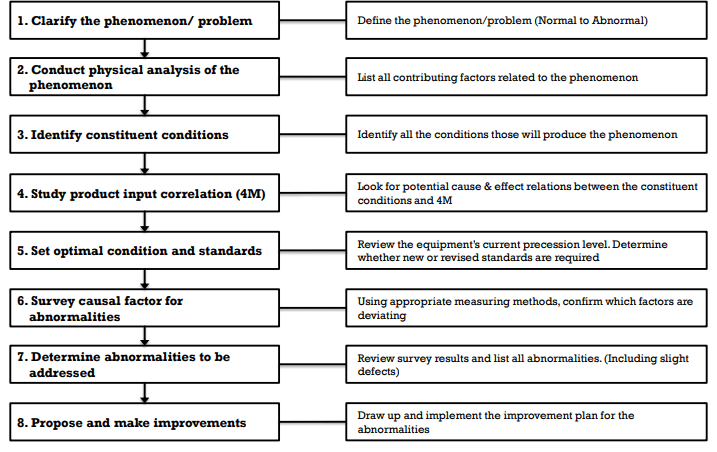
Steps of Preventive Maintenence
Effectiveness of Maintenance
Reliability of the Equipment, Standard of Maintenance, Repair Work Done(MTBF)

Maintainability(MTTR)
Support System, The Skill of the Technical Staff, The Complexity of Failure, The Availability of Spare Parts
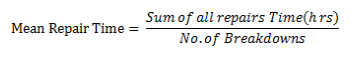
Severity of Breakdowns
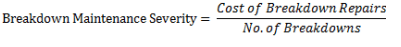
Maintenance Overhead
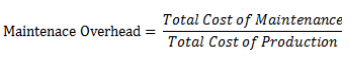
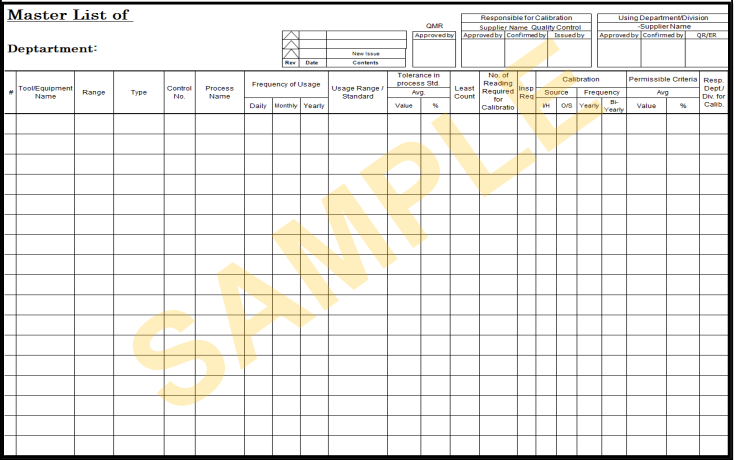
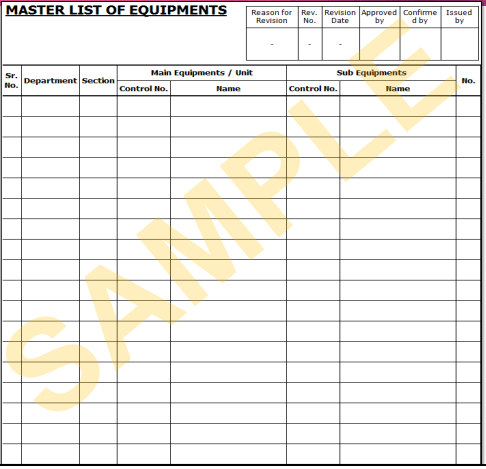
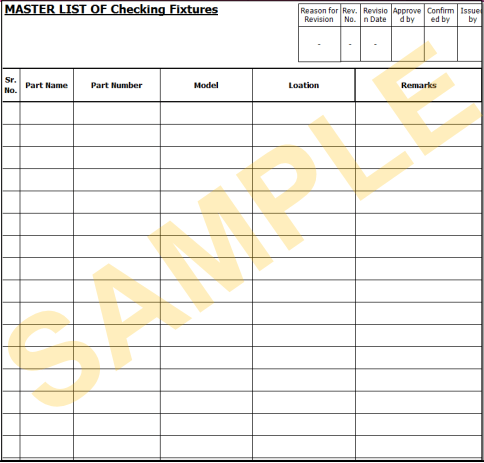
Planned Maintenance – Procedure
I. Master List of (it must include all the possible info i.e. location, usage range, etc)
- QA Devices
- Production Equipment
- Measuring and Monitoring Tools/Devices
II. Make Pre-Operational checks of Production Equipments - Machines- Equipment Operation Standards-To Operate Machine
- Machines- Pre-Operational check sheet-on resuming operation, on shit change or decide by experts
- Molds/Dies-Changeover inspection criteria-on changing of molds
It Must Include the Cleaning(No dust, No Stain, No, NO Dirt, No Debris, etc as per autonomous STD),
Oiling, Lubrication other parameters like bolt tight, pressure check, temperature check, safety items, etc.
III. Make Regular Inspection and Calibration Plans and Execute them accordingly - QA Devices
- Measuring and Monitoring Tools/Devices
IV. Make Periodic Maintenance of Production Equipment(Machine, Molds/Dies) - Planning- Frequency-Hand books, Experts, Usage
- Check Sheet Making-Check Points-Same as above
- Execution
V. Leger of Maintenance, Calibration of all the Equipments
Unplanned Maintenance
In case of abnormality(unplanned Maintenance)
- Maintenance Request
- The repair Control Sheet record the detail of the problem and countermeasures with analysis and control record accordingly
Economical View of Planned Maintenance
Well, Planned preventive maintenance results in higher production, more revenues, and higher profit.
Profit P = S.Q – (CF + Q.CV)
Profit P = Q (S – CV) – CF
Q is the production quantity
S is the unit sale price
CV is a unit variable cost
CFis fixed cost
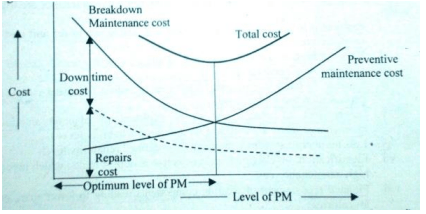
These approaches may effectively reduce both planned and unplanned maintenance occurrences, hence enhancing equipment efficiency and minimizing operational expenses.



