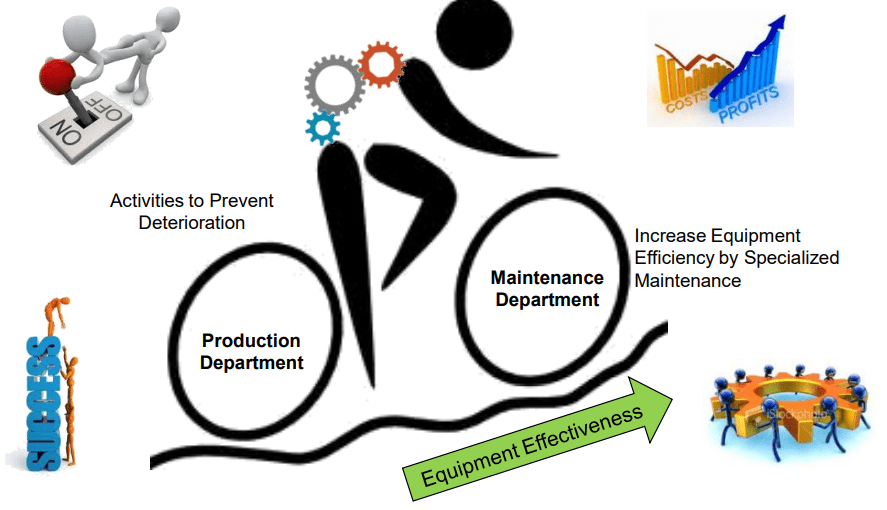
The organizational process aims to achieve a continuous and overall increase in equipment effectiveness by actively engaging and involving all employees. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a complete and systematic approach to equipment maintenance and management that attempts to optimize industrial processes’ operating efficiency, productivity, and overall effectiveness. TPM was created in Japan as part of the Total Quality Management (TQM) and Lean manufacturing revolutions. The core tenet of TPM is to include all employees in the maintenance and upgrading of equipment, so fostering a sense of shared responsibility throughout the firm.
T: Total– Entire Production Life Cycle of equipment, Overall Equipment Efficiency, Covers All departments and participation of all employees
P: Productive-Pursuit of maximization of the efficiency of the production system; not only productivity but it sets goals for;
Zero Accidents
Zero Breakdowns
Zero Defects
M: Maintenance-Making of survival of the Production System
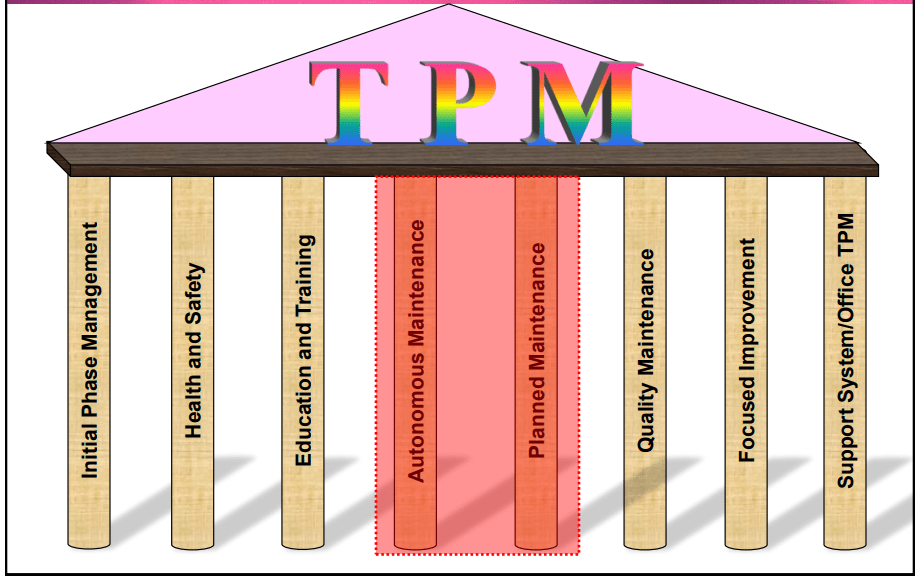
TPM Pillars
The concept of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is commonly organized into a framework consisting of eight core pillars. These pillars serve as distinct dimensions that encompass various facets of equipment management and the pursuit of continual improvement.
TPM and 5-Ms
Man, Money, Materials, Methods, and Machines are the five Ms. Total Productive Maintenance is yet another method for increasing output and reducing losses in any company by enhancing equipment efficiency. All 5Ms of management may be addressed if all eight pillars of TPM are managed wisely.
- Machines (Equipment) – Autonomous Maintenance (Jishu Hozen); Planned MaintenanceMen (People) – Safety & Health; Education & Training
- Materials
- (a) Inputs – Focused Improvement (Kobetsu Kaizen)
- (b) Output – Quality Maintenance; Initial Phase Management
- Methods – (Manufacturing Systems, Procedures) – Kobetsu Kaizen, Jishu Hozen, Initial Phase Management
- Money – Kobetsu Kaizen, Support System/Office TPM
Equipment Deterioration
Natural Deterioration (Extend Life Time)- Corrective Maintenance
- Prevent errors by improving operability
- Improve maintainability and Repair Quality
- Improve safety and reliability
Accelerated Deterioration (Eliminate Causes) – Establish Basic Condition
- Cleaning: Eliminate all dust & dirt
- Lubrication: Keep lubricants clean and replenished
- Tightening: Keep nuts and bolts secure
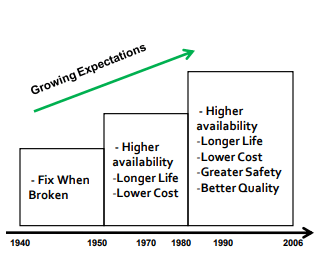
How Would You Proceed?
Unplanned corrective measures refer to actions taken in response to unforeseen circumstances or following instances of mechanical failure or malfunction to provide the necessary information. Planned maintenance has two main components:
- Autonomous Maintenance by the Production Department
- Specialized(Preventive) Maintenance by the Maintenance Department