The maintenance of excellent product quality and the avoidance of faults depend heavily on the early detection of issues during the production process. The significance of identifying issues during manufacturing as well as the numerous inspection techniques used in that industry will be covered in this article.
What is a Problem?
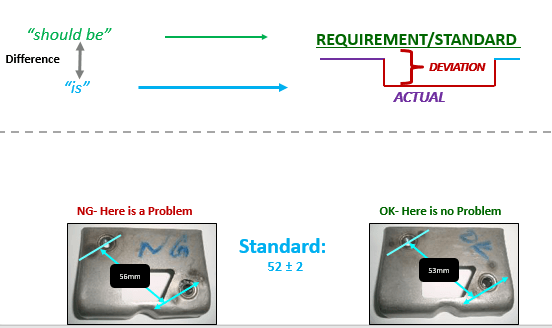
The perceived gap between the Existing State and a Desired State.
What is Cause and Effect?
The cause is the reason something happens, and the effect is what happens as a result.
There can be multiple causes of an effect
“Effects” are dependent on “causes”
Causes are “ Factors” of Effect
An Effect can be a cause for another effect
Example: “Traffic Jam” is the effect of “traffic Accidents”, “Heavy Rain”, and “long queues”, and a cause for “going Late to School”
What is an Inspection?
Inspection is the process of Measuring, examining, and Gauging or otherwise comparing a unit with the applicable requirements.
What is the purpose of Inspection?
Inspection is necessary to meet the customer’s requirements. and protect the product from defects Certainly, some product defects cannot be detected or corrected at the final stages of manufacture.
Purpose
- Acceptance or rejection of the product or lot
- To check production effectiveness
- To ensure customer satisfaction
Inspection Methods
Types of Inspection Method
Visual Inspection- The process of a visible defect by visual examination such as Appearance, Rust, Burrs, Color, Scratches, White Marks, etc.
By using measuring Tools – These measurements are measured as part of the inspection procedure for such a part to see if they meet specifications. Such as Dimensional Measurements etc.
By using Inspection Jigs – Quality control Jigs are essential tools for inspection and quality control. To make sure that components and products adhere to particular quality requirements and tolerances, these specialized tools and fixtures were created. Profile check on Quality Assurance Jigs etc.
By Fitting in CBU- Like Segi, Dankaku, Rio Kaku etc. by installing in CBU(complete body unit)
By Comparing with the Master Sample – By Comparing with limited samples or CKD parts.
Types of Inspection
Final Inspection:
Inspection of the parts after their complete manufacturing and before delivery.
In-Process Inspection:
Inspection of the part after each process(sub-process), can be visual or upon some check sheet as per requirement. Upon each process(sub-process), the following chemistry will be exercised.
Receive Good Make Good Deliver Good
Incoming Inspection
Inspection of Purchased Parts(sub-suppliers), Child Parts, CKD Parts, Supply Parts, and Materials to ensure supplier compliance with specifications and contractual agreements.
Source Inspection
Inspection of purchased parts at the supplier’s facility by a customer representative to ensure supplier compliance with specifications and contractual agreements.
Delivery Inspection
Inspection of delivered parts at customers’ facilities by suppliers
What are Parts Inspection Criteria?
[System/Device and Parts], which set forth acceptance criteria to be applied to the inspection of individual constituent parts of a product.
- Master Samples, Limit Samples, CKD Parts, etc.
- Parts Inspection Standards
Matters Must be Specified in Parts Inspection Criteria?
- Part number/ part name
- Inspection item
- Item importance
- Quality judgment criteria
- Inspection method
- Inspection plan and Frequency
- Data format
- Inspection section



