
KAIZEN: Improving an understanding of Japanese business philosophy
- What is Kaizen?
- The Principles of Kaizen
- The Kaizen Process
- What are some benefits of Kaizen?
- Implementation of Kaizen
- Future of Kaizen
- Conclusion
What is Kaizen?
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy that means positive change or continuous improvements in the production processes of an organization and its output such as product.
History: In collaboration with Japanese management expert Dr. W. Edward Deming introduced Kaizen in Japan after World War 2 when the country needed to rebuild its economy.
How Kaizen is considered a continuous improvement in an organization?
In the current era of a competitive business environment, continuous improvement is important because the goal of Kaizen is to make small changes and improvements within a company by the use of efficient equipment and elimination of waste through different procedures and techniques. Many companies utilize the Kaizen Concept to make improvements such as Toyota, Toyota encourages all employees to identify problems and create their solutions.
Principles of Kaizen
Kaizen has a core value in a company to improve its production efficiency such as continuous improvements. Kaizen helps to improve the organization’s potential, consistency, and reliability in methodologies that help to identify problems, causes, and their solutions.
There are five principles of Kaizen discussed here:
Know Your Customer
To ensure that the company can create value for its consumers, the key principle holds that it is important to identify the interests and desires of the target market. From the initial purchase through any future customer care that may be required, a better customer experience is made possible thanks to the understanding.
Let it Flow
To achieve this objective everyone in the organization has to contribute towards a zero-waste environment. Zero waste signifies the amount of time, movement, and raw resources used to complete an activity. Kaizen assists in value creation that is most effective,
Go to Gemba
Gemba means “the real place” in the world of business. The office or factory floor are examples of places where work is done or value is produced. According to the kaizen principles, value can only be created when events take place. Therefore, it is imperative to physically arrive there.
Be Empower
To achieve exceptional efficiency, the management must be in agreement with the team about a set of objectives. Setting goals that are applicable at all levels of the organization hierarchy, giving people the tools and procedures they need to complete their responsibilities, and putting in place a mechanism for developmental feedback all contribute to the cause.
Being Transparent
Kaizen promotes dealing with feedback and improvement easier because everyone can see the numbers. Employees who are transparent are more likely to receive constructive criticism and remain optimistic and open-minded.
The Kaizen Process
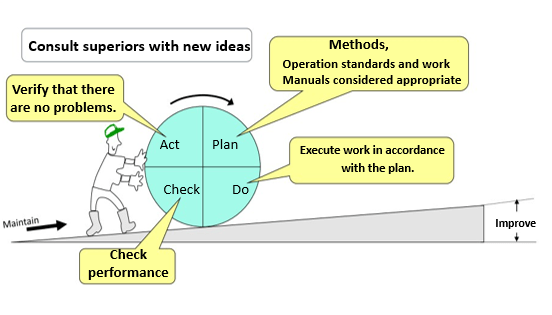
PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Action)
In our daily work, the methods, which are determined to be appropriate From experience and know-how, are standardized.
The 5S Methodology
Also frequently inquired about is what the term “kaizen 5S” means. It pertains to the five processes of improvement—Sort, Straighten, Sweep, Standardize, and Sustain, which are frequently employed in lean manufacturing. Each of these phases is followed by a 5S event, one day at a time.
Benefits of Kaizen
Teamwork: The advantage of the Kaizen is to engage everyone to identify and solve the problem collectively.
Targets:
Everyone involved in the firm, from top managers to floor laborers, suppliers, and customers, is included in this attitude of continuous improvement. The majority of business types can benefit from the kaizen technique. It rewards and recognizes the employees’ contributions, giving them a sense of value and belonging.
Efficiency:
Because there are no interruptions and the procedures are standardized, everyone working on the project can focus on it effectively. Additionally, limiting any time, effort, or movement waste guarantees that more work is completed without going beyond.
Cost Reduction
Kaizen helps companies save and lower costs.
Implementation of Kaizen
There are many examples of sectors where Kaizen can be used to improve their production efficiency and changes in manufacturing for better quality products.
Service Sectors: Describe how Kaizen principles can be used in service-based industries like banks and hotels.
Medical Care: Describe how Kaizen is used in healthcare settings to enhance patient care and lower errors.
Computer and software programming: Demonstrate how Kaizen can be applied to IT operations and the development of agile software.
Future of Kaizen
Kaizen has a bright future as businesses adopt technology more and more and adjust to shifting market conditions. One noteworthy development is the use of automation and artificial intelligence in Kaizen processes, which allows for increased data-driven decision-making and the spotting of improvement opportunities on a never-before-seen scale. In addition, Kaizen initiatives are increasingly incorporating sustainability concerns, linking continuous improvement with ethical environmental behavior.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kaizen is a permanent and revolutionary idea that enables businesses to start a journey of continuous development. Its guiding concepts of constant improvement, standardization, and waste reduction have been successfully applied in a variety of fields and businesses. Kaizen continues to be a guiding light for companies as they navigate the dynamic landscape of the global economy by providing a disciplined method for increasing productivity, cutting costs, and raising the quality of goods and services.


